# 一.循环体中为什么不用+?
# 1.测试代码
public class Basic_21_String {
public static void main(String[] args) {
long s1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
new Basic_21_String().addMethod();
System.out.println("使用 + 拼接:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - s1));
s1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
new Basic_21_String().stringBuilderMethod();
System.out.println("使用 StringBuilder 拼接:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - s1));
}
public String addMethod() {
String result = "";
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
result += (i + "武培轩");
}
return result;
}
public String stringBuilderMethod() {
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
result.append(i).append("武培轩");
}
return result.toString();
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
使用 + 拼接:17615 使用 StringBuilder 拼接:9
# 2.源码分析
从字节码层面来看下,为什么循环体中字符串拼接 StringBuilder 比 + 快这么多
先进入 class 目录
cd /Users/qinyingjie/Documents/idea-workspace/ant/ant-basic/target/classes/com/xiaofei/antbasic/basic_question
1
执行脚本
javap -c Basic_21_String
1
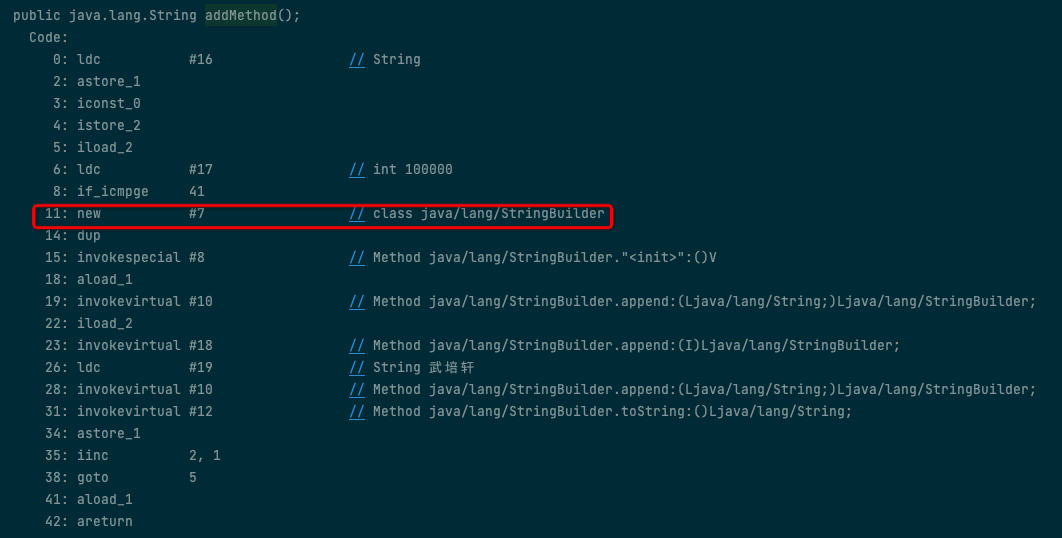
仔细查看字节码文件,可以发现,addMethod 方法中,在循环体内部,每次都会 new 新的 StringBuilder 对象,根据 java 的内存管理和垃圾回收,这种方式,性能差.可以发现+的底层其实是 new 了一个新的 StringBuilder 对象进行处理.StringBuilder 是线程不安全的可变长字符串,可以提高对字符串的处理性能.
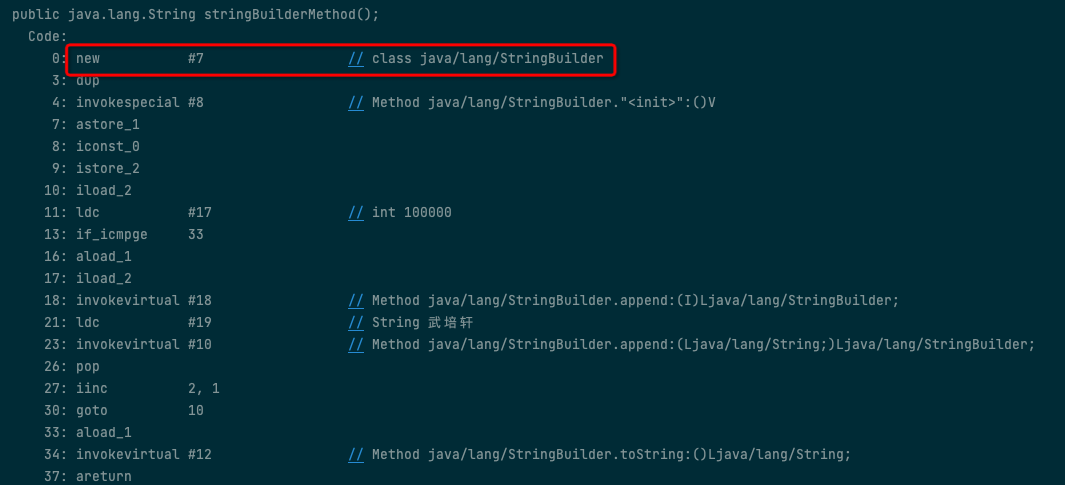
查看 stringBuilderMethod 方法,可以看到只会 new 一次 StringBuilder 对象,性能好,优先选择 StringBuilder 进行字符串的拼接.
# 3.开发建议
《阿里巴巴 Java 开发手册》时,发现有一条是关于循环体中字符串拼接的建议

# 二.字符串常量池
# 1.常量比较
public class Basic_14_String_01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "愉快的菠萝";
String s2 = "愉快的";
String s3 = "菠萝";
String s4 = "愉快的菠萝";
String s5 = s2 + s3;
//在常量池中,一个常量只会对应一个地址,另外对于基本数据类型(byte,short,char,int,float,double,long,boolean)来说,他们也是作为常量在方法区中的常量池里面。
System.out.println(s1 == s4);
//是因为+在编译时两边都是字符串常量是会有优化,会给它合并到一起,它也是“愉快的菠萝”这个字符串,所以它是一个地址。
System.out.println((s1 == "愉快的" + "菠萝"));
//s2+s3 在+两边的是个变量,编译时不知道具体的值,不能优化,而且它会转化为StringBuilder类型通过append方法拼接,可以通过反编译查看,它是一个新的对象所以地址不同
System.out.println(s1 == s5);
System.out.println(System.identityHashCode(s1));
System.out.println(System.identityHashCode(s4));
System.out.println(System.identityHashCode(s5));
/**
*
* 打印结果
* true
* true
* false
* 1879034789
* 1879034789
* 875827115
*/
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
# 2.final 比较
public class Basic_14_String_02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
final String s1 = "愉快的菠萝";
final String s2 = "愉快的";
final String s3 = "菠萝";
final String s4 = "愉快的菠萝";
final String s5 = s2 + s3;
//在常量池中,一个常量只会对应一个地址,另外对于基本数据类型(byte,short,char,int,float,double,long,boolean)来说,他们也是作为常量在方法区中的常量池里面。
System.out.println(s1 == s4);
//是因为+在编译时两边都是字符串常量是会有优化,会给它合并到一起,它也是“愉快的菠萝”这个字符串,所以它是一个地址。
System.out.println((s1 == "愉快的" + "菠萝"));
//s2+s3 在+两边的是个常量
System.out.println(s1 == s5);
System.out.println(System.identityHashCode(s1));
System.out.println(System.identityHashCode(s4));
System.out.println(System.identityHashCode(s5));
/**
*
* 打印结果
*
* true
* true
* true
* 1879034789
* 1879034789
* 1879034789
*
≈
*/
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
# 3.static 比较
public class Basic_14_String_03 {
public static final String fs2; // 常量A
public static final String fs3; // 常量B
static {
fs2 = "愉快";
fs3 = "菠萝";
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
final String fs1 = "愉快的菠萝";
final String fs4 = "愉快的菠萝";
final String fs5 = fs2 + fs3; //fs5是不确定的
System.out.println(fs1 == fs4);
System.out.println((fs1 == "愉快的" + "菠萝"));
System.out.println(fs1 == fs5);
System.out.println(System.identityHashCode(fs1));
System.out.println(System.identityHashCode(fs4));
System.out.println(System.identityHashCode(fs5));
}
/**
*
* 打印结果
* true
* true
* false
* 2128227771
* 2128227771
* 1702297201
*/
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
# 4.new 比较
public class Basic_14_String_04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String ns1 = new String("愉快的菠萝");
String ns2 = new String("愉快的");
String ns3 = new String("菠萝");
String ns4 = new String("愉快的菠萝");
String ns5 = ns2 + ns3;
System.out.println(ns1 == ns4);
System.out.println((ns1 == "愉快的" + "菠萝"));
System.out.println(ns1 == ns5);
System.out.println(System.identityHashCode(ns1));
System.out.println(System.identityHashCode(ns4));
System.out.println(System.identityHashCode(ns5));
}
/**
*
* 打印结果 通过new 出来的字符串,都是不一样的对象,所以地址都是不一样的
*
* false
* false
* false
* 2128227771
* 1702297201
* 1996181658
*
*/
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
# 三.常用编码
# 1.list 转 str
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("a");
list.add("b");
list.add("c");
System.out.printf("集合:");
list.stream().forEach(a ->
System.out.printf(a)
);
String str = StringUtils.join(list, ",");
System.out.println();
System.out.println("字符串:" + str);
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
# 2.首字母大小写
//首字母大写
StringUtils.capitalize(str)
//首字母小写
StringUtils.uncapitalize(str1)
1
2
3
4
5
2
3
4
5
# 3.lang3 包
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.apache.commons/commons-lang3 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-lang3</artifactId>
<version>3.9</version>
</dependency>
1
2
3
4
5
6
2
3
4
5
6
# 4.format 方法
1.常用转换符号
| 符号 | 说明 | 符号 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|---|
| %s | 字符串类型 | %c | 字符类型 |
| %d | 十进制整数 | %x | 十六进制整数 |
| %o | 八进制整数 | %b | Boolean 类型 |
| %f | 浮点数 | %a | 十六进制浮点数 |
| %g | 通用浮点数 | %e | 指数形式 |
| %h | 散列码 | %% | 百分号 |
| %n | 换行 |
public class Basic_13_String_format_01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//%s %c
String str;
str = String.format("Hello %s%c", "world", '!');
System.out.println(str);
//%b
str = String.format("%b", 10 > 3);
System.out.println(str);
str = String.format("%b", 2 >= 3);
System.out.println(str);
//%d %x %o
str = String.format("十进制:%d", 10);
System.out.println(str);
str = String.format("十六进制:%x", 10);
System.out.println(str);
str = String.format("八进制:%o", 10);
System.out.println(str);
//%f %a %g %e
str = String.format("浮点数:%f", 3.14159);
System.out.println(str);
str = String.format("十六进制浮点数:%a", 3.14159);
System.out.println(str);
str = String.format("通用浮点类型:%g", 3.1415926);
System.out.println(str);
str = String.format("指数形式:%e", 3.14159);
System.out.println(str);
//%h %% %n
str = String.format("散列码:%h", "123456");
System.out.println(str);
str = String.format("百分之九十:%d%%", 90);
System.out.println(str);
str = String.format("测试到此结束!%n");
System.out.println(str);
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
2.常用标识
| 标识 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| + | 使得正数表示出正号,负数加不加为所谓,都可以表示出负号。 |
| - | 左对齐,不够位数的地方补上空格 |
| 0 | 在数字位数不够的地方补上 0 |
| 空格 | 在位数不够的地方补上空格 |
| , | 对数字分组,三位一隔,只可以用于十进制 |
| ( | 使用括号将去掉负号的负数包含进来 |
| # | 让十六进制的数字加上 ox,八进制的数字加上。: 辅助%x 和%o 的使用,相当于一种对数字进制的补充说明提示 |
| < | 格式化前一个转换符所描述的参数 |
public class Basic_13_String_format_02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//+号的用法
String str;
str = String.format("数字的正负表示:%+d %d %+d %d", 8, 8, -8, -8);
System.out.println(str);
//-的用法
str = String.format("左对齐:%-6d", 8);
System.out.println(str);
//0的用法
str = String.format("缺位补零:%06d", 8);
System.out.println(str);
//' '空格的用法
str = String.format("缺位补空格:% 6d", 8);
System.out.println(str);
str = String.format("缺位补空格:% 6d", -8);
System.out.println(str);
//,的用法
str = String.format("数字分组:%,d", 123456789);
System.out.println(str);
//(的用法
str = String.format("括号用法:%(d", -8888);
System.out.println(str);
str = String.format("括号用法:%(d", 8888);
System.out.println(str);
//#的用法
str = String.format("#括号用法(十六进制):%#x", 12);
System.out.println(str);
str = String.format("#括号用法(八进制):%#o", 12);
System.out.println(str);
//<的用法
str = String.format("<括号用法:%f %<3.1f", 3.14, 3.2);
//"%<3.1f"作用的对象是前一个"%f"所作用的对象
System.out.println(str);
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
# 5.List 转 String
/**
* list转string
*
* @author : kwan
* @date : 2022/8/3
*/
public class Basic_09_String {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
//list转string
String str = String.join("','", list);
//list转set
Set<String> set = new HashSet<>(list);
//set转list
List<String> sets = new ArrayList<>(set);
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
# 6.字符串日期互转
/**
* 日期转字符串
*
* @author : qinyingjie
* @date : 2022/8/3
*/
public class Basic_01_DateToString {
public static void main(String[] args) {
dateToString(new Date());
}
public static String dateToString(Date date) {
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");
System.out.println(sdf.format(date));
sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
System.out.println(sdf.format(date));
sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy年MM月dd日 HH:mm:ss");
System.out.println(sdf.format(date));
return sdf.toPattern();
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
/**
* 字符串转日期
*
* @author : qinyingjie
* @date : 2022/8/3
*/
public class Basic_02_StringToDate {
public static void main(String[] args) {
stringToDate();
}
public static void stringToDate() {
String string = "2003-10-14 10:10:20";
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
try {
System.out.println(sdf.parse(string));
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
/**
* 字符串转日期 字符串短了 抛异常
*
* @author : qinyingjie
* @date : 2022/8/3
*/
public class Basic_03_StringToDate {
public static void main(String[] args) {
stringToDate();
}
public static void stringToDate() {
String string = "2003-10-14";
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
try {
System.out.println(sdf.parse(string));
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
/**
* 字符串转日期 字符串长了可以解析
*
* @author : qinyingjie
* @date : 2022/8/3
*/
public class Basic_04_StringToDate {
public static void main(String[] args) {
stringToDate();
}
public static void stringToDate() {
String string = "2003-10-14 10:10:20";
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");
try {
System.out.println(sdf.parse(string));
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
# 7.字符串是否在枚举中
public boolean isNeedApostrophe() {
return !Arrays.stream(SqlFilter.NumericDataType.values())
.filter(value -> this.dataType.equalsIgnoreCase(value.getType())).findFirst()
.isPresent();
}
public enum NumericDataType {
TINYINT("TINYINT"),
SMALLINT("SMALLINT"),
MEDIUMINT("MEDIUMINT"),
INT("INT"),
INTEGER("INTEGER"),
BIGINT("BIGINT"),
FLOAT("FLOAT"),
DOUBLE("DOUBLE"),
DECIMAL("DECIMAL"),
NUMERIC("NUMERIC");
private String type;
NumericDataType(String type) {
this.type = type;
}
public String getType() {
return type;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
# 8.leftPad 拼接补充
cardOrder.setCardOrderNum("B" + new DateTime().toString("yyyyMMddHHmmss") + StringUtils.leftPad("" + new SecureRandom().nextInt(100), 3, "0"));
1
# 9.String.join()使用方式
String result = String.join("-",“a”,“b”,“c”,“d”);
输出结果如下:a-b-c-d
1
2
2
# 10.字符串截取
public static void main(String[] args) {
String sql = "select * from `davinci0.3`.view view left join `davinci0.3`.view1 view1 on view.id=view1.view_id";
int left = sql.indexOf("left");
System.out.println(sql.substring(sql.indexOf("left"), sql.length() - 1));
}
1
2
3
4
5
2
3
4
5
← 02-body参数变了 04-JDK新特性 →
