# 一.基本介绍
# 1.介绍
Nginx(发音为"engine x")是一款高性能、轻量级的开源 Web 服务器和反向代理服务器,它具有以下特点和功能:
- 高性能:Nginx 被设计为能够处理大量并发连接而不显著增加系统负担。它采用异步事件驱动的架构,可以有效地处理高流量的 Web 请求。
- 负载均衡:Nginx 支持负载均衡,可以将请求分发到多个后端服务器,以提高网站性能和可用性。
- 反向代理:Nginx 可以充当反向代理,将客户端请求转发到后端服务器,隐藏后端服务器的真实 IP 地址,增加安全性和可扩展性。
- 静态文件服务:Nginx 可以高效地提供静态文件(如 HTML、CSS、JavaScript、图像等)的服务,减轻应用服务器的负担。
- SSL/TLS 支持:Nginx 支持加密通信,可以配置 SSL/TLS 来保护数据传输的安全性。
- URL 重写:Nginx 允许对 URL 进行灵活的重写和转发,以实现友好的 URL 结构和路由。
- 缓存:Nginx 可以缓存静态内容和动态内容,提高响应速度并减轻后端服务器的负担。
- 访问控制:Nginx 可以实施访问控制、IP 黑名单、基本身份验证等安全性措施。
- 模块化架构:Nginx 使用模块化的架构,允许用户通过插件和模块来扩展其功能。
Nginx 通常被用于构建高性能的 Web 服务器环境,特别适合处理大流量的网站和应用。它在互联网上广泛使用,并已成为许多大型网站和应用的关键组件之一。
# 2.功能
以下是 Nginx 的一些主要功能:
Web 服务器: Nginx 可以作为一个快速、高性能的 Web 服务器,可以直接处理和提供静态和动态内容。
反向代理: Nginx 可以作为反向代理服务器,接收客户端请求并将其转发到后端服务器,用于负载均衡、缓存、SSL 终端等。
负载均衡: Nginx 可以将来自客户端的请求分发到多个后端服务器,实现负载均衡,提高应用的可扩展性和性能。
HTTP 缓存: Nginx 可以缓存静态和动态内容,减轻后端服务器的负载,提高响应速度。
SSL 终端: Nginx 可以处理 SSL/TLS 连接,用于终止和处理加密通信,减轻后端服务器的计算负担。
反向代理缓存: Nginx 可以作为反向代理缓存,将动态内容缓存到本地,减少对后端服务器的请求,提高响应速度。
动态内容处理: Nginx 可以处理 FastCGI、uWSGI、SCGI 等协议,用于处理动态内容如 PHP、Python、Ruby 等。
限流和速率控制: Nginx 可以实施请求速率控制和限流,以防止服务器过载。
安全性: Nginx 提供安全功能如防止恶意请求、DDoS 攻击防护等。
虚拟主机: Nginx 支持虚拟主机配置,可以在一个服务器上托管多个域名。
自定义模块: Nginx 支持自定义模块开发,可以根据需求添加自定义的功能和扩展。
事件驱动: Nginx 使用事件驱动的异步架构,可以处理大量并发连接,提供出色的性能。
日志记录: Nginx 可以记录详细的访问日志,方便监控和分析。
Nginx 是一个功能强大的服务器软件,适用于多种应用场景,如 Web 服务器、反向代理、负载均衡、缓存、安全保护等。它在大型互联网公司和企业中被广泛使用,提供了高性能和稳定性。
# 3.无法重启
杀死已有的 Nginx 进程:
如果打算重新启动 Nginx,首先需要停止或杀死已经运行的 Nginx 进程。
首先尝试优雅地停止 Nginx 服务:
sudo systemctl stop nginx
如果 systemctl 停止命令没有成功(或者手动启动了 Nginx),可以使用 kill 命令来终止进程:
sudo kill -9 8507 20453 20454 20455 20456 20457 20458 20459 20460
这些是运行 Nginx 的进程 ID,需要替换它们为实际看到的进程 ID。
确认所有 Nginx 进程已停止:
使用以下命令确认没有 Nginx 进程还在运行:
ps aux | grep nginx
如果输出中不再有 Nginx 进程,那么它们已经停止。
# 启动
sudo systemctl start nginx
# 查看状态
sudo systemctl status nginx
2
3
4
5
# 4.返回 499
大概率是服务端接口需要太长的时间,导致 nginx 打印 499
# 二.常规相关命令
# 1.查看相关
#查看nginx在哪
whereis nginx
# 查看所有nginx进程
ps aux | grep nginx
#查看状态
systemctl status nginx
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
# 2.启停状态
#启动nginx
systemctl start nginx
#停止 nginx
systemctl stop nginx
#重新加载配置
systemctl reload nginx
#重启 nginx
systemctl restart nginx
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
# 3.设置开机启动
#设置开机启动
systemctl enable nginx
#关闭开机启动设置
systemctl disable nginx
2
3
4
5
# 4.检查配置是否正确
nginx -t
# 5.查看版本
nginx -V
# 6.重新加载
#进入nginx可执行目录sbin下,输入命令,不用重启
nginx -s reload
2
# 三.常见配置
Nginx 的主配置文件是 nginx.conf,这个配置文件一共由三部分组成,分别为全局块、events 块和 http 块。在 http 块中,又包含 http 全局块、多个 server 块。每个 server 块中,可以包含 server 全局块和多个 location 块。在同一配置块中嵌套的配置块,各个之间不存在次序关系。
# 1.配置目录
#从 / 根目录下查找文件名为 nginx.conf 的文件
find / -name nginx.conf
#从/etc 目录下查找文件名为 nginx.conf 的文件
find /etc -name nginx.conf
#检查配置文件
nginx -t
#目录
/etc/nginx
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
# 2.执行目录
/usr/sbin/nginx
# 3.站点目录
站点目录是配置的,根据配置文件来的
指定根目录
location / {
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
2
3
4
root /usr/share/nginx/html; #就是站点目录
# 4.配置文件的优先级
启动时可以指定配置文件
首先,说明结论:同一目录下存在多个配置文件时,Nginx是按照文件的名称先后顺序依次读取的!
#验证配置文件
/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -tc /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -t -c /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
#指定配置文件启动
/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -c /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
#指定配置文件重启
/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s reload -c /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
#说明:-c 参数指定运行nginx系统的自定义配置文件。
#若加:使用自定义配置文件。
#若不加:使用默认的nginx.conf(一般位于/usr/local/conf/nginx.conf,具体以实际情况为准)
nginx -c /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
# 5.websocket
要在 Nginx 中开通 WebSocket,需要在 Nginx 配置文件中添加相应的配置。
以下是一个简单的 Nginx 配置文件示例,其中开通了 WebSocket:
http {
# ...
map $http_upgrade $connection_upgrade {
default upgrade;
'' close;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name example.com;
location /ws/ {
proxy_pass http://backend_server/ws/;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection "upgrade";
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
在这个配置文件中,map 指令用于将 HTTP 请求头中的 Upgrade 和 Connection 字段映射到 Nginx 的变量中,proxy_pass 指令用于将请求转发到后端服务器,proxy_http_version 指令用于指定使用 HTTP 1.1 协议进行转发,proxy_set_header 指令用于设置请求头字段。
具体来说,proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade; 指令用于将 HTTP 请求头中的 Upgrade 字段设置为 $http_upgrade 变量的值,proxy_set_header Connection $connection_upgrade; 指令用于将 HTTP 请求头中的 Connection 字段设置为 $connection_upgrade 变量的值。
这样,当客户端发送一个 WebSocket 请求时,Nginx 就会将其转发到后端服务器,并将请求头中的 Upgrade 和 Connection 字段设置为 WebSocket 需要的值,从而成功开通了 WebSocket。
# 6.设置超时时间
http {
proxy_connect_timeout 300; #单位秒
proxy_send_timeout 300; #单位秒
proxy_read_timeout 300; #单位秒
proxy_buffer_size 16k;
proxy_buffers 4 64k;
proxy_busy_buffers_size 128k;
proxy_temp_file_write_size 128k;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
# 7.多前端配置
多站点配置
访问新空间:https://meihua150.cn/
访问图书管理:https://meihua150.cn/book
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
index index.html index.htm;
location / {
# root /usr/share/nginx/html;
# index index.html index.htm;
}
location /book/ {
alias /usr/share/nginx/book/; # 静态文件路径
autoindex on; # 启用目录索引,相当于开启权限
index index.html index.htm;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
# 8.proxy_ignore_client_abort
将 499 的返回修正为服务端的返回
proxy_ignore_client_abort on;
# 9.$http_host
在 Nginx 配置中,$http_host和$host都是内置变量,它们都与 HTTP 请求中的Host头有关,但它们的含义有所不同。
$http_host:这个变量包含客户端请求中的Host头的值。它是客户端指定的,即用户在浏览器地址栏中输入的域名或 IP 地址,加上可能的端口号。例如,如果用户访问http://example.com:8080,那么$http_host的值就是example.com:8080。$host:这个变量包含当前请求的服务器名称,它是由 Nginx 的配置决定的。在大多数情况下,$host的值与$http_host相同,但在某些配置下,如使用server_name指令指定了特定的域名时,$host可能与$http_host不同。区别:
$http_host直接反映了客户端的请求,而$host则可能受到 Nginx 配置的影响。- 在大多数情况下,
$http_host和$host的值是相同的,但在特定的 Nginx 配置下,它们可能不同。 - 使用
$http_host可以确保后端服务器接收到的是客户端原始的请求信息,而使用$host可能会导致后端服务器接收到的是 Nginx 服务器的配置信息。
联系:
- 两者都是 Nginx 中用于设置
Host头的变量,它们都与 HTTP 请求的Host头有关。 - 在配置反向代理时,正确地选择使用
$http_host还是$host对于确保后端服务器能够正确处理请求至关重要。
- 两者都是 Nginx 中用于设置
# 10.多location同一个proxy_pass
location ~* ^/(api|/files|v1|test)(.*)$ {
proxy_pass http://10.111.111.1111:8080;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header Host $http_host;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection "upgrade";
proxy_redirect off;
client_max_body_size 600M;
client_body_buffer_size 600M;
uwsgi_send_timeout 1800;
uwsgi_connect_timeout 1800;
uwsgi_read_timeout 1800;
proxy_read_timeout 1800;
proxy_connect_timeout 1800;
proxy_send_timeout 1800;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
# 11.使用域名代理注意事项
rewrite的神奇使用
location /chat-api {
proxy_pass http://156.99.22.191:9988;
}
location /chat-api {
rewrite ^/chat-api$ /$1 break;
proxy_pass http://aichatbot-chat-server-s0-ai-dev-1:9988;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
# 6. 应用场景
使用
$http_host的场景:- 当后端服务需要根据
Host头来决定路由时,使用$http_host可以确保后端服务接收到的是客户端的原始请求信息。 - 在负载均衡和内容分发网络(CDN)中,使用
$http_host可以确保请求被正确地路由到后端服务。
- 当后端服务需要根据
使用
$host的场景:- 当 Nginx 服务器的配置需要覆盖客户端的
Host头时,例如在某些特定的负载均衡或重写规则中,使用$host可以确保后端服务接收到的是 Nginx 服务器的配置信息。
- 当 Nginx 服务器的配置需要覆盖客户端的
# 四.日志与文件
# 1.看正常日志
tail -f /var/log/nginx/access.log
# 2.错误日志
tail -f /var/log/nginx/error.log
# 3.日志 docker
通过容器查看日志
# 4.配置文件
cat /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
# 5.传输 dist(部署前端)
目录:
/usr/share/nginx/html
dist方式:
# 传输
scp /Users/qinyingjie/Downloads/000000-新空间/知识图谱/dist.zip root@47.104.164.9:/usr/share/nginx/html
# 解压
cd /usr/share/nginx/html
unzip dist.zip
# 移动
cd /usr/share/nginx/html/dist
sudo mv * /usr/share/nginx/html
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
非压缩文件:
# 源文件
scp -r /Users/qinyingjie/Downloads/dist/* root@47.104.164.9:/usr/share/nginx/html
2
# 五.配置 https
# 1.nginx 检查
nginx -V
# 2.上传证书
# crt文件
scp /Users/qinyingjie/Downloads/meihua150.cn_1724254338/meihua150.cn.crt root@47.104.164.9:/etc/nginx
# key文件
scp /Users/qinyingjie/Downloads/meihua150.cn_1724254338/meihua150.cn.key root@47.104.164.9:/etc/nginx
2
3
4
5
# 3.http 的配置
# For more information on configuration, see:
# * Official English Documentation: http://nginx.org/en/docs/
# * Official Russian Documentation: http://nginx.org/ru/docs/
user nginx;
worker_processes auto;
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log;
pid /run/nginx.pid;
# Load dynamic modules. See /usr/share/doc/nginx/README.dynamic.
include /usr/share/nginx/modules/*.conf;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
'$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
'"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log main;
sendfile on;
tcp_nopush on;
tcp_nodelay on;
keepalive_timeout 65;
types_hash_max_size 2048;
include /etc/nginx/mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
# Load modular configuration files from the /etc/nginx/conf.d directory.
# See http://nginx.org/en/docs/ngx_core_module.html#include
# for more information.
include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf;
server {
listen 80;
server_name wwww.qinyingjie.top;
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
# Load configuration files for the default server block.
include /etc/nginx/default.d/*.conf;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8080/;
}
location ~ .*\.(gif|jpg|jpeg|png|jfif|webp)$ {
root /kwan/;
autoindex on ;
}
error_page 404 /404.html;
location = /40x.html {
}
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
# 4.https 的配置
# For more information on configuration, see:
# * Official English Documentation: http://nginx.org/en/docs/
# * Official Russian Documentation: http://nginx.org/ru/docs/
user nginx;
worker_processes auto;
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log;
pid /run/nginx.pid;
# Load dynamic modules. See /usr/share/doc/nginx/README.dynamic.
include /usr/share/nginx/modules/*.conf;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
'$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
'"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log main;
sendfile on;
tcp_nopush on;
tcp_nodelay on;
keepalive_timeout 65;
types_hash_max_size 2048;
include /etc/nginx/mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
# Load modular configuration files from the /etc/nginx/conf.d directory.
# See http://nginx.org/en/docs/ngx_core_module.html#include
# for more information.
include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf;
server {
listen 80;
#请填写绑定证书的域名
server_name www.qinyingjie.top;
#把http的域名请求转成https
return 301 https://$host$request_uri;
}
server {
#SSL 默认访问端口号为 443
listen 443 ssl;
#请填写绑定证书的域名
server_name www.qinyingjie.top;
#请填写证书文件的相对路径或绝对路径
ssl_certificate www.qinyingjie.top_bundle.crt;
#请填写私钥文件的相对路径或绝对路径
ssl_certificate_key www.qinyingjie.top.key;
ssl_session_timeout 5m;
#请按照以下套件配置,配置加密套件,写法遵循 openssl 标准。
ssl_ciphers ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE:ECDH:AES:HIGH:!NULL:!aNULL:!MD5:!ADH:!RC4;
#请按照以下协议配置
ssl_protocols TLSv1.2 TLSv1.3;
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
location / {
#网站主页路径。此路径仅供参考,具体请您按照实际目录操作。
#例如,您的网站主页在 Nginx 服务器的 /etc/www 目录下,则请修改 root 后面的 html 为 /etc/www。
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8080/;
}
location ~ .*\.(gif|jpg|jpeg|png|jfif|webp)$ {
root /kwan/;
autoindex on ;
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
# 5.验证与加载
# 检查配置是否正确(常用)
nginx -t
# 加载配置
nginx -s reload
2
3
4
5
# 6.查看日志
# 正常log
cat /var/log/nginx/access.log
# 全局查看
cat /var/log/nginx/error.log
# 尾部查看
tail -f /var/log/nginx/error.log
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
# 六.proxy_pass
# 1.总结汇总
结论:
- 如果 proxy_pass 末尾有斜杠/,proxy_pass 不拼接 location 的路径
- 如果 proxy_pass 末尾无斜杠/,proxy_pass 会拼接 location 的路径
# 2.proxy_pass 末尾有斜杠
location /api/ {
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8000/;
}
2
3
请求地址:http://localhost/api/test
转发地址:http://127.0.0.1:8000/test
# 3.proxy_pass 末尾无斜杠
location /api/ {
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8000;
}
2
3
请求地址:http://localhost/api/test
转发地址:http://127.0.0.1:8000/api/test
# 4.proxy_pass 包含路径,且末尾有斜杠
location /api/ {
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8000/user/;
}
2
3
请求地址:http://localhost/api/test
转发地址:http://127.0.0.1:8000/user/test
# 5.proxy_pass 包含路径,末尾无斜杠
location /api/ {
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8000/user;
}
2
3
请求地址:http://localhost/api/test
转发地址:http://127.0.0.1:8000/usertest
# 6.改写路径
location /test/server {
rewrite ^/test(.*)$ $1 break;
proxy_pass http://xxxx.xxx.xx.xx:8320$1;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection "upgrade";
proxy_redirect off;
client_max_body_size 600M;
client_body_buffer_size 600M;
uwsgi_send_timeout 1800;
uwsgi_connect_timeout 1800;
uwsgi_read_timeout 1800;
proxy_read_timeout 1800;
proxy_connect_timeout 1800;
proxy_send_timeout 1800;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
# 7.优先级
# ^~优先匹配代理路径
location ^~ /new-space/kwan/ {
proxy_pass http://43.139.90.182:9000/new-space/kwan/;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
# 七.Rewrite 模块
# 1.工作原理
Rewrite 模块的指令包括break, if, return, rewrite, set等。Rewrite 指令会根据 PCRE 正则匹配重写 URI,然后发起内部跳转再匹配 location,或者直接做 30x 重定向返回客户端。如果新 URI 包含协议信息,如http://或https://,则会直接返回客户端重定向。
# 2.Rewrite Flag 参数
last:停止处理任何 rewrite 相关的指令,立即用替换后的新 URI 开始下一轮的 location 匹配。break:停止处理任何 rewrite 的相关指令,直接用新的 URI 进一步处理请求。redirect:返回 302 临时重定向。permanent:返回 301 永久重定向。
# 3. 隐藏真实目录结构
使用 rewrite 可以隐藏服务器上的真实文件路径和目录结构,增加安全性,防止攻击者通过直接访问文件路径获取敏感信息。例如,可以通过以下配置实现:
rewrite ^/api/(.*)$ /backend/$1 break;
这样,所有的/api/请求都会被重写到/backend/目录下,而外界无法直接通过 URL 猜测真实的文件路径。
# 4. 防止盗链
通过 rewrite 实施防盗链策略,防止其他网站直接链接到本站的资源,减轻服务器负载,提高资源的安全性。例如:
rewrite ^/images/(.*)$ /notfound.gif if-not-referer($http_referer, "http://www.yoursite.com");
这个规则会检查 Referer 头,如果不是来自指定的站点,则重写到一个占位符图片。
# 5. HTTP 到 HTTPS 的强制重定向
通过 rewrite 将 HTTP 请求强制重定向到 HTTPS,确保数据在传输过程中的安全性。例如:
server {
listen 80;
server_name example.com;
rewrite ^ https://$server_name$request_uri? permanent;
}
2
3
4
5
这个配置会将所有的 HTTP 请求重定向到 HTTPS。
# 6. 条件性重写
可以根据请求中的条件来选择是否进行重写,例如,只有特定 IP 范围的请求才允许进行某种操作。例如:
map $remote_addr $allowed {
default 0;
192.168.1.1 1;
}
location /admin {
rewrite ^/admin(.*)$ /access_denied last;
if ($allowed = 0) {
return 403;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
这个配置会阻止未授权的 IP 访问/admin目录。
# 7. 避免敏感信息泄露
通过 rewrite 可以限制对某些敏感信息或文件的访问,确保只有授权用户能够获取特定内容。例如:
location ~* ^/sensitive/.*\.php$ {
deny all;
}
2
3
这个配置会阻止所有用户访问/sensitive/目录下的 PHP 文件。
# 8.通配符讲解
=:用于不含正则表达式的 uri 前,要求请求字符串与 uri 严格匹配,如果匹配成功,就停止继续向下搜索并立即处理该请求~:用于表示 uri 包含正则表达式,并且区分大小写~*:用于表示 uri 包含正则表达式,并且不区分大小写^~:用于不含正则表达式的 uri 前,要求 Nginx 服务器找到标识 uri 和请求。字符串匹配度最高的 location 后,立即使用此 location 处理请求,而不再使用 location 块中的正则 uri 和请求字符串做匹配。
# 八.牛逼特性
# 1.域名配置
server_name www.qinyingjie.top;
# 2.图片不展示
location ~ .*\.(gif|jpg|jpeg|png|jfif)$ {
proxy_pass https://www.qinyingjie.top;
root /kwan/;
autoindex on;
}
2
3
4
5
# 3.负载均衡
1.轮训
upstream open-api-test-category{
server 10.250.16.111:8195;
server 10.250.16.111:8196;
}
location / {
proxy_pass http://open-api-test-category/;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
2.权重
upstream open-api-test-category{
server 10.250.16.111:8195 weight=1;
server 10.250.16.111:8196 weight=3;
}
location / {
proxy_pass http://open-api-test-category/;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
3.hash
upstream open-api-test-category{
server 10.250.16.111:8195;
server 10.250.16.111:8196;
ip_hash;
}
location / {
proxy_pass http://open-api-test-category/;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
# 4.动静分离
location ~ .*\.(gif|jpg|jpeg|png|jfif|webp|mp4)$ {
root /kwan/ ;
autoindex on ;
}
2
3
4
# 5.正向代理
- 正向代理是代理服务器位于客户端和目标服务器之间的一种代理方式。
- 客户端请求发送到正向代理服务器,然后由代理服务器将请求转发到目标服务器。
- 正向代理隐藏了客户端的真实 IP 地址,使目标服务器只能看到代理服务器的 IP 地址。
- 正向代理通常用于访问被封锁或受限制的内容,或者用于增加安全性和隐私。
- 比如 VPN,原理就是使用了正向代理,隐藏了客户端的信息。
# 6.反向代理
- 反向代理是代理服务器位于目标服务器和客户端之间的一种代理方式。
- 客户端将请求发送到反向代理服务器,然后代理服务器根据规则将请求转发给后端的目标服务器。
- 反向代理隐藏了目标服务器的真实 IP 地址,客户端只能看到代理服务器的 IP 地址。
- 反向代理通常用于负载均衡、缓存、安全性和高可用性方面,可以提高网站的性能和可靠性。
- 比如部署的服务,使用反向代理,隐藏服务端信息,避免被攻击。
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
proxy_pass http://localhost:8080/;
}
2
3
4
5
后端接口反向代理:
location /newspace/ {
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8118; # 代理到本地地址
proxy_set_header Host $host; # 设置代理请求的Host头
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr; # 将客户端真实IP传递给后端
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; # 传递X-Forwarded-For头
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme; # 传递请求使用的协议
proxy_set_header Connection ""; # 连接头,防止后端关闭连接
proxy_http_version 1.1; # 使用HTTP/1.1
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade; # 允许WebSockets
proxy_set_header Connection "upgrade"; # 允许WebSockets
proxy_read_timeout 86400; # 设置代理读超时
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
实战:
proxy_set_header Authorization $http_authorization;
代理时,头部携带 Authorization 参数
location /api/server/ {
rewrite ^/api(.*)$ $1 break;
proxy_pass http://11.11.1.11:8320;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Authorization $http_authorization;
proxy_set_header Connection "upgrade";
proxy_redirect off;
client_max_body_size 600M;
client_body_buffer_size 600M;
uwsgi_send_timeout 1800;
uwsgi_connect_timeout 1800;
uwsgi_read_timeout 1800;
proxy_read_timeout 1800;
proxy_connect_timeout 1800;
proxy_send_timeout 1800;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
# 7.root 和 alias 区别
最基本的区别:alias 指定的目录是准确的,root 是指定目录的上级目录,并且该上级目录要含有 location 指定名称的同名目录。另外,根据前文所述,使用 alias 标签的目录块中不能使用 rewrite 的 break。
alias 虚拟目录配置中,location 匹配的 path 目录如果后面不带"/“,那么访问的 url 地址中这个 path 目录后面加不加”/“不影响访问,访问时它会自动加上”/“;
但是如果 location 匹配的 path 目录后面加上”/“,那么访问的 url 地址中这个 path 目录必须要加上”/“,访问时它不会自动加上”/“。如果不加上”/“,访问就会失败!
root 目录配置中,location 匹配的 path 目录后面带不带”/",都不会影响访问。
在 nginx 配置中的良好习惯是:
- 在 location /中配置 root 目录;
- 在 location /path 中配置 alias 虚拟目录。
#直观理解如下形式:
location /dev/{
alias /web/dev/doc/; #这个查找文件的路径直接是/web/dev/doc/
}
location /dev/{
root /web/dev/doc/; #这个查找文件的路径应该是/web/dev/doc/dev
}
# 这里使用root配置 如果访问 192.168.2.3/pak/a.html 则对应的路径为:/usr/local/pak/a.html
# 通过root配置则location配置的/pak/一定是要在root对应的/usr/local/目录下要有的目录
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
# 8.限流功能
nginx 提供了两种限流方式,
- 一种是限制请求速率
- 一种是限制连接数量
限制请求速率:nginx 的 ngx_http_limit_req_module 模块提供限制请求处理速率的能力,使用了漏桶算法(leaky bucket algorithm)。我们可以想像有一只上面进水、下面匀速出水的桶,如果桶里面有水,那刚进去的水就要存在桶里等下面的水流完之后才会流出,如果进水的速度大于水流出的速度,桶里的水就会满,这时水就不会进到桶里,而是直接从桶的上面溢出。对应到处理网络请求,水代表从客户端来的请求,而桶代表一个队列,请求在该队列中依据先进先出(FIFO)算法等待被处理。漏的水代表请求离开缓冲区并被服务器处理,溢出代表了请求被丢弃并且永不被服务。
漏桶算法
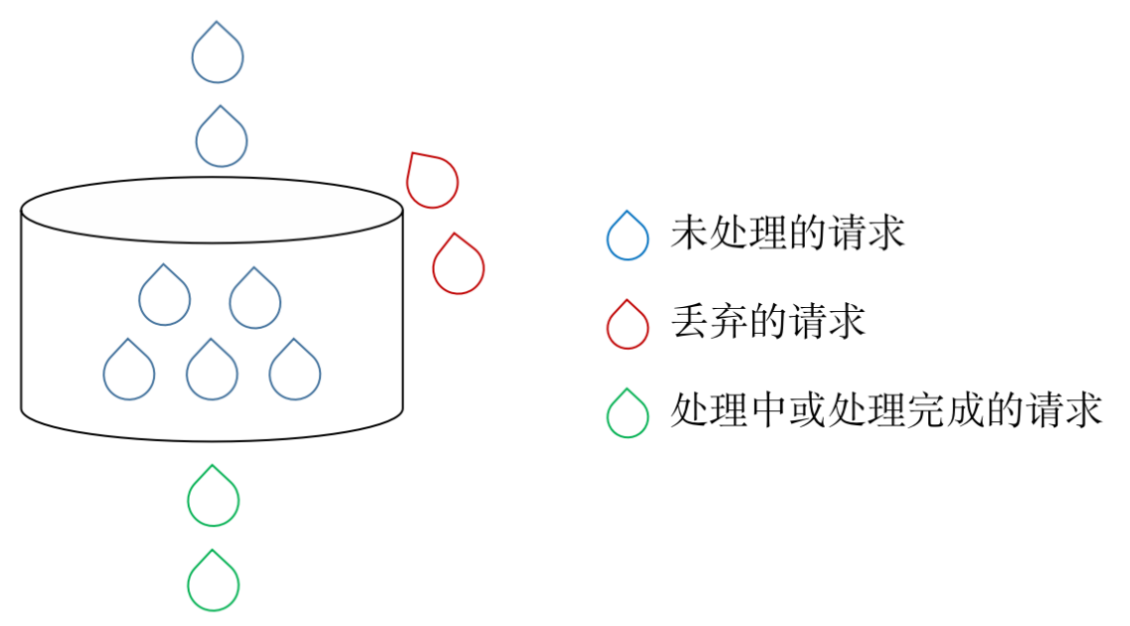
limit_req_zone $binary_remote_addr zone=mylimit:10m rate=2r/s;
server {
location ~* \.(html)$ {
limit_req zone=mylimit;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
limit_req_zone 用于设置限流和共享内存区域的参数,格式为:limit_req_zone key zone rate。
- key:定义限流对象,$binaryremote_addr 是 nginx 中的变量,表示基于 remote_addr(客户端 IP) 来做限流,binary 是二进制存储。使用 $binary_remote_addr 而不是 $remote_addr 是因为二进制存储可以压缩内存占用量。 $remote_addr 变量的大小从 7 到 15 个字节不等,而 $binary_remote_addr 变量的大小对于 IPv4 始终为 4 个字节,对于 IPv6 地址则为 16 个字节。
- zone:定义共享内存区来存储访问信息,访问信息包括每个 IP 地址状态和访问受限请求 URL 的频率等。zone 的定义又分为两个部分:由 zone= 关键字标识的区域名称,以及冒号后面的区域大小。myLimit:10m 表示一个大小为 10M,名字为 myLimit 的内存区域。1M 能存储 16000 个 IP 地址的访问信息,myLimit 大概可以存储约 160000 个地址。nginx 创建新记录的时候,会移除前 60 秒内没有被使用的记录,如果释放的空间还是存储不了新的记录,会返回 503 的状态码。
- rate:设置最大的访问速率。rate=2r/s(为了好模拟,rate 设置的值比较小),表示每秒最多处理 2 个请求。事实上 nginx 是以毫秒为粒度追踪请求的,rate=2r/s 实际上是每 500 毫秒 1 个请求,也就是说,上一个请求完成后,如果 500 毫秒内还有请求到达,这些请求会被拒绝(默认返回 503,如果想修改返回值,可以设置 limit_req_status)。
limit_req_zone 只是设置限流参数,如果要生效的话,必须和 limit_req 配合使用。limit_req 的格式为:limit_req zone=name [burst=number] [nodelay]。 上面的例子只简单指定了 zone=mylimit,表示使用 mylimit 这个区域的配置,在请求 html 文件时进行限流。我们可以理解为这个桶目前没有任何储存水滴的能力,到达的所有不能立即漏出的请求都会被拒绝。如果我 1 秒内发送了 10 次请求,其中前 500 毫秒 1 次,后 500 毫秒 9 次,那么只有前 500 毫秒的请求和后 500 毫秒的第一次请求会响应,其余请求都会被拒绝。
limit_req_zone $binary_remote_addr zone=mylimit:10m rate=2r/s;
server {
location ~* \.(html)$ {
limit_req zone=mylimit burst=5;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
burst 表示在超过设定的访问速率后能额外处理的请求数。当 rate=2r/s 时,表示每 500ms 可以处理一个请求。burst=5 时,如果同时有 10 个请求到达,nginx 会处理第 1 个请求,剩余 9 个请求中,会有 5 个被放入队列,剩余的 4 个请求会直接被拒绝。然后每隔 500ms 从队列中获取一个请求进行处理,此时如果后面继续有请求进来,如果队列中的请求数目超过了 5,会被拒绝,不足 5 的时候会添加到队列中进行等待。我们可以理解为现在的桶可以存 5 滴水:
limit_req_zone $binary_remote_addr zone=mylimit:10m rate=2r/s;
server {
location ~* \.(html)$ {
limit_req zone=mylimit burst=5 nodelay;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
nodelay 表示不延迟。设置 nodelay 后,第一个到达的请求和队列中的请求会立即进行处理,不会出现等待的请求。需要注意的是,虽然队列中的 5 个请求立即被处理了,但是队列中的位置依旧是按照 500ms 的速度依次被释放的。后面的 4 个请求依旧是被拒绝的,长期来看并不会提高吞吐量的上限,长期吞吐量的上限是由设置的 rate 决定的。
nginx 限流使用了令牌桶算法:

漏桶算法和令牌桶算法都是用于实现流量控制和限流的算法,但它们的原理和适用场景略有不同。
漏桶算法: 漏桶算法模拟了一个漏桶,请求被认为是水滴,以固定的速率流出(漏出)系统。如果流入的请求速率超过了漏桶的容量,多余的请求将会被丢弃或者等待下一个时间段。漏桶算法适用于平滑流量,防止系统被大量突发流量压垮。但是,对于短时间内的突发流量,漏桶算法并不是特别有效,因为它无法快速处理瞬时大量的请求,而只能以固定的速率处理。
令牌桶算法: 令牌桶算法也是一种流量控制算法,它基于一个令牌桶的概念。令牌以一定的速率被添加到桶中,每个请求在处理之前需要获取一个令牌,如果没有可用的令牌,则请求将被暂时阻塞或丢弃。令牌桶算法可以适应瞬时的突发流量,因为当桶中积累足够多的令牌时,可以快速处理突发请求,而不会受限于固定的速率。这使得令牌桶算法更适合处理突发流量的情况。
所以,总的来说,漏桶算法更适合平滑流量,而令牌桶算法更适合应对突发流量。在实际应用中,可以根据需求选择合适的算法来实现流量控制和限流。
