# 一.队列概述
# 1.概述
计算机科学中,queue 是以顺序的方式维护的一组数据集合,在一端添加数据,从另一端移除数据。习惯来说,添加的一端称为尾,移除的一端称为头,就如同生活中的排队买商品
先定义一个简化的队列接口
public interface Queue<E> {
/**
* 向队列尾插入值
* @param value 待插入值
* @return 插入成功返回 true, 插入失败返回 false
*/
boolean offer(E value);
/**
* 从对列头获取值, 并移除
* @return 如果队列非空返回对头值, 否则返回 null
*/
E poll();
/**
* 从对列头获取值, 不移除
* @return 如果队列非空返回对头值, 否则返回 null
*/
E peek();
/**
* 检查队列是否为空
* @return 空返回 true, 否则返回 false
*/
boolean isEmpty();
/**
* 检查队列是否已满
* @return 满返回 true, 否则返回 false
*/
boolean isFull();
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
# 2.链表实现
下面以单向环形带哨兵链表方式来实现队列

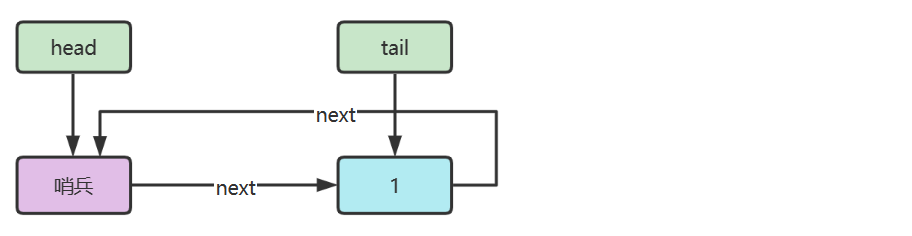
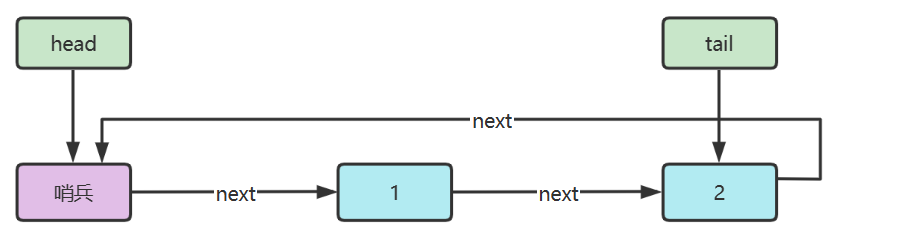
代码
public class LinkedListQueue<E>
implements Queue<E>, Iterable<E> {
private static class Node<E> {
E value;
Node<E> next;
public Node(E value, Node<E> next) {
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
}
private Node<E> head = new Node<>(null, null);
private Node<E> tail = head;
private int size = 0;
private int capacity = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
{
tail.next = head;
}
public LinkedListQueue() {
}
public LinkedListQueue(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
}
@Override
public boolean offer(E value) {
if (isFull()) {
return false;
}
Node<E> added = new Node<>(value, head);
tail.next = added;
tail = added;
size++;
return true;
}
@Override
public E poll() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
Node<E> first = head.next;
head.next = first.next;
if (first == tail) {
tail = head;
}
size--;
return first.value;
}
@Override
public E peek() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
return head.next.value;
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty() {
return head == tail;
}
@Override
public boolean isFull() {
return size == capacity;
}
@Override
public Iterator<E> iterator() {
return new Iterator<E>() {
Node<E> p = head.next;
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return p != head;
}
@Override
public E next() {
E value = p.value;
p = p.next;
return value;
}
};
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
# 3.环形数组实现
好处
- 对比普通数组,起点和终点更为自由,不用考虑数据移动
- “环”意味着不会存在【越界】问题
- 数组性能更佳
- 环形数组比较适合实现有界队列、RingBuffer 等

下标计算
例如,数组长度是 5,当前位置是 3 ,向前走 2 步,此时下标为 $(3 + 2)%5 = 0$
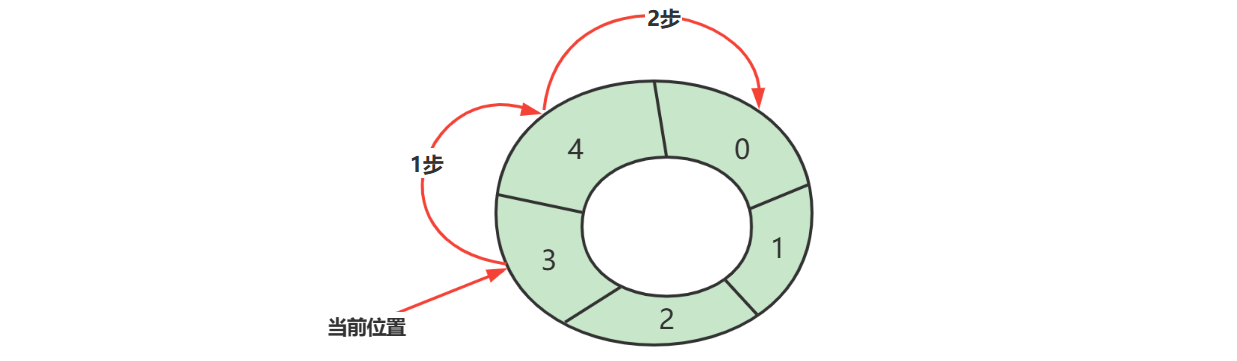
$$ (cur + step) % length $$
- cur 当前指针位置
- step 前进步数
- length 数组长度
注意:
- 如果 step = 1,也就是一次走一步,可以在 >= length 时重置为 0 即可
判断空
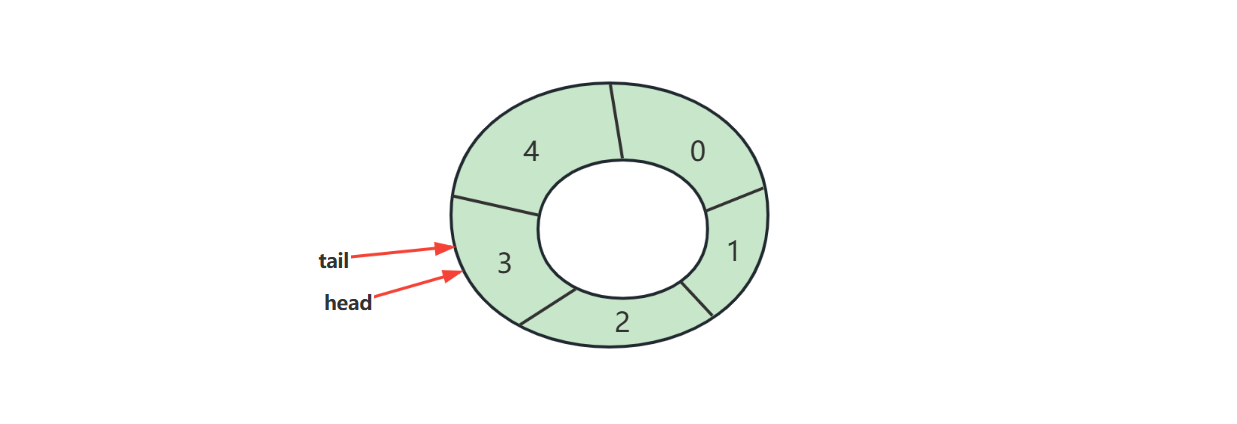
判断满
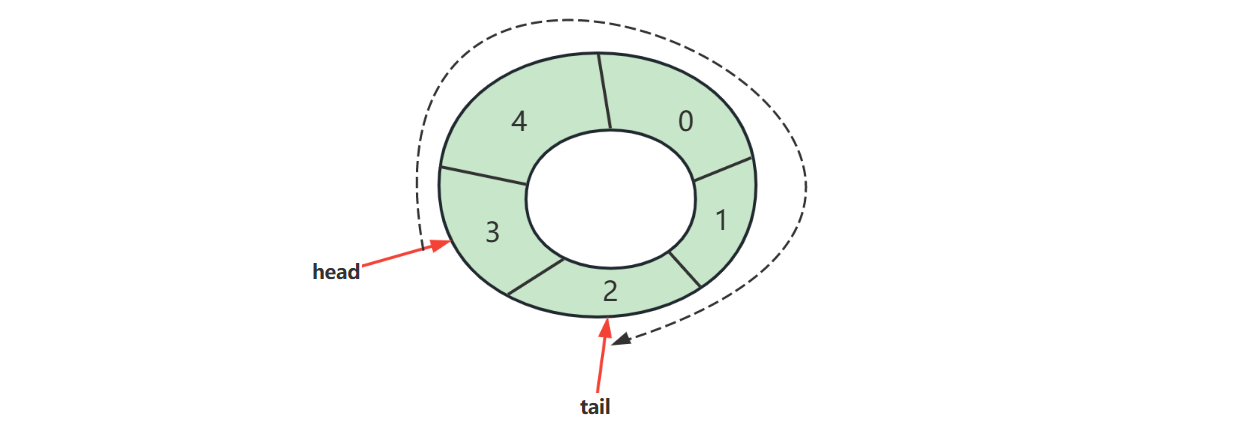
满之后的策略可以根据业务需求决定
- 例如我们要实现的环形队列,满之后就拒绝入队
代码
public class ArrayQueue<E> implements Queue<E>, Iterable<E>{
private int head = 0;
private int tail = 0;
private final E[] array;
private final int length;
@SuppressWarnings("all")
public ArrayQueue(int capacity) {
length = capacity + 1;
array = (E[]) new Object[length];
}
@Override
public boolean offer(E value) {
if (isFull()) {
return false;
}
array[tail] = value;
tail = (tail + 1) % length;
return true;
}
@Override
public E poll() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
E value = array[head];
head = (head + 1) % length;
return value;
}
@Override
public E peek() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
return array[head];
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty() {
return tail == head;
}
@Override
public boolean isFull() {
return (tail + 1) % length == head;
}
@Override
public Iterator<E> iterator() {
return new Iterator<E>() {
int p = head;
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return p != tail;
}
@Override
public E next() {
E value = array[p];
p = (p + 1) % array.length;
return value;
}
};
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
判断空、满方法 2
引入 size
public class ArrayQueue2<E> implements Queue<E>, Iterable<E> {
private int head = 0;
private int tail = 0;
private final E[] array;
private final int capacity;
private int size = 0;
@SuppressWarnings("all")
public ArrayQueue2(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
array = (E[]) new Object[capacity];
}
@Override
public boolean offer(E value) {
if (isFull()) {
return false;
}
array[tail] = value;
tail = (tail + 1) % capacity;
size++;
return true;
}
@Override
public E poll() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
E value = array[head];
head = (head + 1) % capacity;
size--;
return value;
}
@Override
public E peek() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
return array[head];
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
@Override
public boolean isFull() {
return size == capacity;
}
@Override
public Iterator<E> iterator() {
return new Iterator<E>() {
int p = head;
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return p != tail;
}
@Override
public E next() {
E value = array[p];
p = (p + 1) % capacity;
return value;
}
};
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
判断空、满方法 3
head 和 tail 不断递增,用到索引时,再用它们进行计算,两个问题
如何保证 head 和 tail 自增超过正整数最大值的正确性
如何让取模运算性能更高
答案:让 capacity 为 2 的幂
public class ArrayQueue3<E> implements Queue<E>, Iterable<E> {
private int head = 0;
private int tail = 0;
private final E[] array;
private final int capacity;
@SuppressWarnings("all")
public ArrayQueue3(int capacity) {
if ((capacity & capacity - 1) != 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("capacity 必须为 2 的幂");
}
this.capacity = capacity;
array = (E[]) new Object[this.capacity];
}
@Override
public boolean offer(E value) {
if (isFull()) {
return false;
}
array[tail & capacity - 1] = value;
tail++;
return true;
}
@Override
public E poll() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
E value = array[head & capacity - 1];
head++;
return value;
}
@Override
public E peek() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
return array[head & capacity - 1];
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty() {
return tail - head == 0;
}
@Override
public boolean isFull() {
return tail - head == capacity;
}
@Override
public Iterator<E> iterator() {
return new Iterator<E>() {
int p = head;
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return p != tail;
}
@Override
public E next() {
E value = array[p & capacity - 1];
p++;
return value;
}
};
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
# 二.队列刷题
# 1.二叉树的层序遍历-力扣 102 题
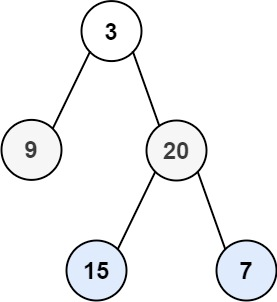
输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
输出:[[3],[9,20],[15,7]]
1
2
2
private static List<List<Integer>> getLists(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) {
return result;
}
LinkedListQueue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedListQueue<>();
queue.offer(root);
int c1 = 1;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
List<Integer> level = new ArrayList<>(); // 保存每一层结果
int c2 = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < c1; i++) {
TreeNode n = queue.poll();
level.add(n.val);
if (n.left != null) {
queue.offer(n.left);
c2++;
}
if (n.right != null) {
queue.offer(n.right);
c2++;
}
}
result.add(level);
c1 = c2;
}
return result;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
